New AI tools that can write student essays require educators to rethink teaching and assessment
https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/impactofsocialsciences/2022/05/17/new-ai-tools-that-can-write-student-essays-require-educators-to-rethink-teaching-and-assessment/
Please take a moment to read the short one-page article. The article includes a paper on learning styles written entirely by an AI program from the prompt, “The construct of ‘learning styles’ is problematic because.” The resulting paper is chilling from the perspective of an educator who is trying to encourage students (especially undergraduate students) to learn to think critically and to write effectively.
In Singapore, we make the students remove and store their watches during exams because they have started using them to communicate and to find answers to exam questions. I’ve abandoned exams for this and other reasons, relying on formative assessments that involve analysis and writing. But what if the students could put a phrase into an application like the GPT-3 tool (https://openai.com/api/) to which this article refers?
When I began my PhD journey, which followed a 1 ½ years of teaching in China and Vietnam, I wanted to study cheating behaviors. I had not taught a single course section out of seven sections in those first 18 months in which at least one student had not obviously cheated—and in many cases, groups of students, as many as five, for example all handing in the same paper. I was dissuaded by my advisor for good reason—why take on a controversial topic that could interfere with achieving my doctoral degree? Now I am rethinking this topic in the context of pedagogy (e.g., experiential learning methods) and assessment. As an aside, the academic integrity issues have occurred everywhere I have taught, including in: Buffalo, NY; Asheville, NC; and Singapore.

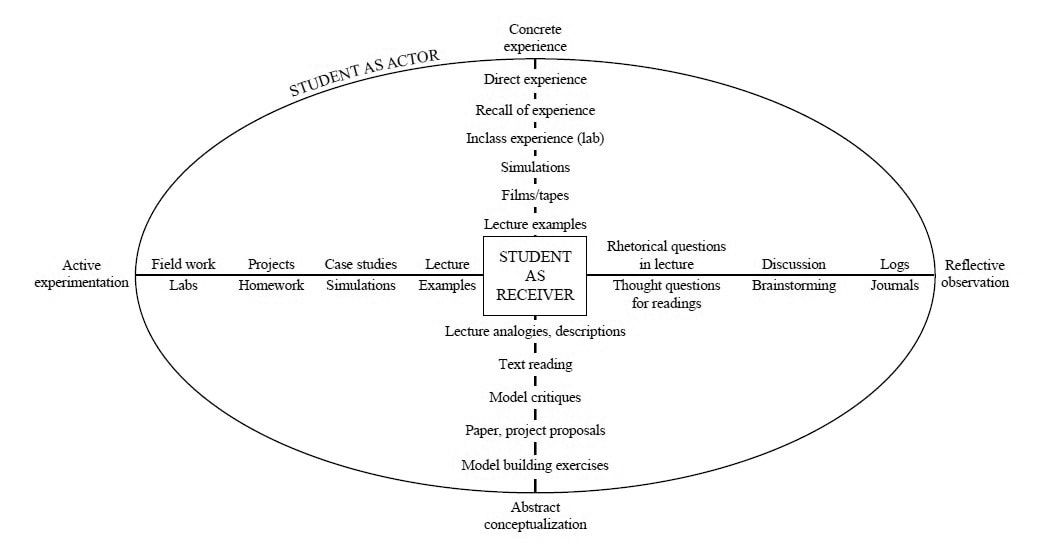



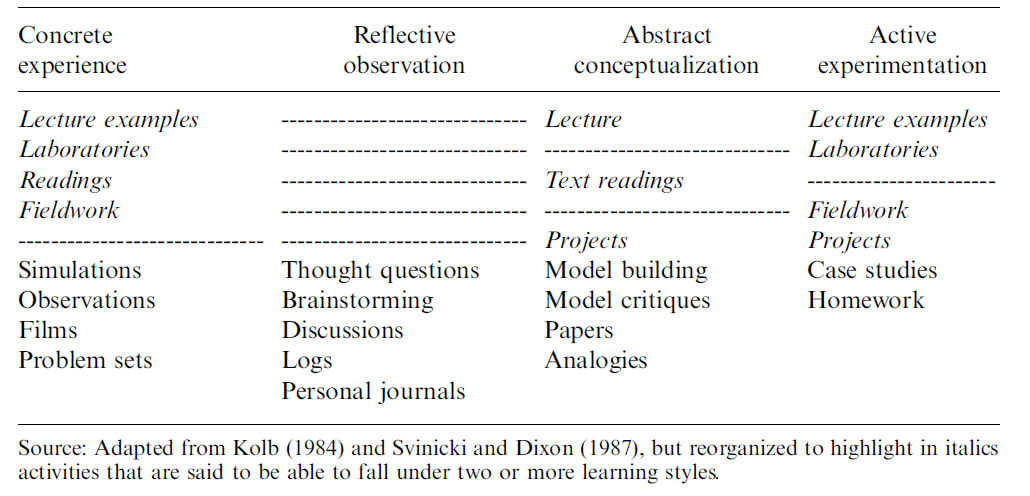

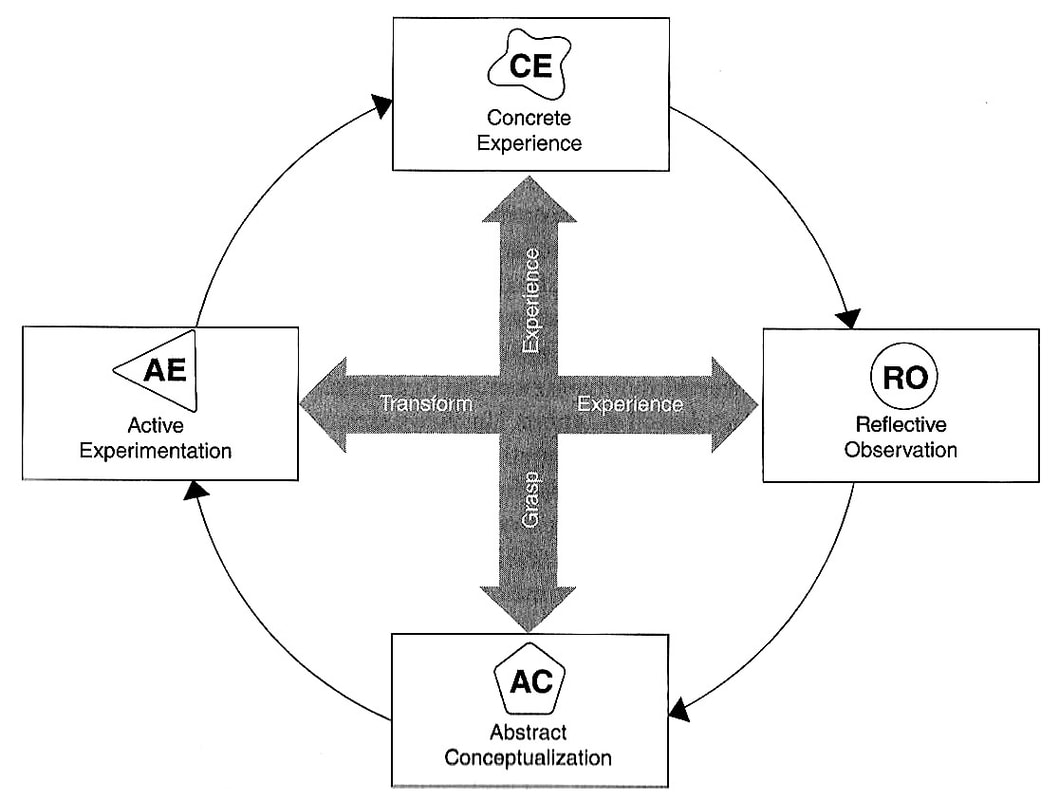
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed