What might be the opposite of active or experiential learning? Educational literature generally defines this opposite method as passive learning, or sometimes traditional learning. Think lectures. Here is one definition of passive learning, "We define a passive mode of engagement as learners being oriented toward and receiving information from the instructional materials without overtly doing anything else related to learning" (Chi & Wylie, 2014, p. 221).
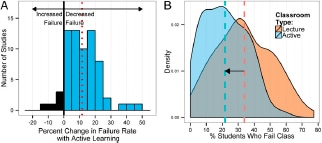
Here is a definition of active learning from another group of authors, "Active learning engages students in the process of learning through activities and/or discussion in class, as opposed to passively listening to an expert. It emphasizes higher-order thinking and often involves group work" (Freeman et al., 2014, pp. 8413-8414). In their analysis of research into the performance of students exposed to active versus passive learning, Freeman et al. (2014) found benefits for active learning.
For my ongoing research, I will take care to use the term active learning when talking to instructors and students in Vietnam. I will be careful to determine what instructors call experiential or active learning in other countries to be certain that my interview and survey responses are valid.
References
Chi, M. T., & Wylie, R. (2014). The ICAP framework: Linking cognitive engagement to active learning outcomes. Educational Psychologist, 49(4), 219-243.
Freeman, S., Eddy, S. L., McDonough, M., Smith, M. K., Okoroafor, N., Jordt, H., & Wenderoth, M. P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(23), 8410-8415.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed